In the rapidly evolving landscape of generative AI, Executives are grappling with understanding the technology’s business implications and associated risks. This guide is designed to demystify generative AI essentials for business leaders.
The buzz around generative AI, especially post the advent of tools like ChatGPT, Bard, Claude, and Midjourney, has left Executives pondering over its significance: Is it merely a technological fad or a transformative business opportunity? Understanding its value to their business is crucial.
ChatGPT’s public version attracted 100 million users within two months, setting a new precedent in AI democratization and becoming the fastest-growing app in history. Its ease of use sets it apart from previous AI technologies. With generative AI, advanced degrees in machine learning are not prerequisites for extracting value; almost anyone capable of asking questions can leverage it. This accessibility is akin to how personal computers or iPhones revolutionized technology, enabling a multitude of applications for diverse audiences.
Generative AI’s power lies in foundation models, which are large neural networks trained on massive amounts of varied data like text and audio. These models are versatile, capable of tasks ranging from summarizing complex technical reports to devising marketing strategies and even generating recipes. However, this versatility can sometimes lead to inaccuracies, highlighting the importance of robust AI risk management.
With appropriate safeguards, generative AI can revolutionize business use cases, enhancing and accelerating existing processes. For instance, in sales, generative AI can offer real-time upselling suggestions during customer calls, drawing from a wide array of data sources. This not only demonstrates its impact on specific job roles but also its potential to augment the productivity of nearly every knowledge worker.
Executives are keen to understand the right time to embrace generative AI. Some view it as an opportunity to outpace competitors by redefining work processes, while others prefer a cautious approach, starting with smaller experiments. It’s crucial for companies to evaluate their readiness in terms of technical expertise, technology and data infrastructure, operational models, and risk management capabilities for effective generative AI integration.
This article aims to assist Executives and their teams in understanding the value generative AI brings and how to embark on this journey. It begins with a primer on the current state of AI and the available technical options. It then explores four example cases of how businesses can engage with generative AI to enhance organizational effectiveness. These cases draw from early adopters’ experiences, offering insights into the spectrum of technology, cost, and operational models. Lastly, the article underscores the executive’s critical role in steering their organization towards success with generative AI.
As the excitement around generative AI grows, it’s imperative for C-suite Executives to proceed with informed and strategic speed. This guide aims to provide business leaders with a well-rounded introduction to the promising realm of generative AI.
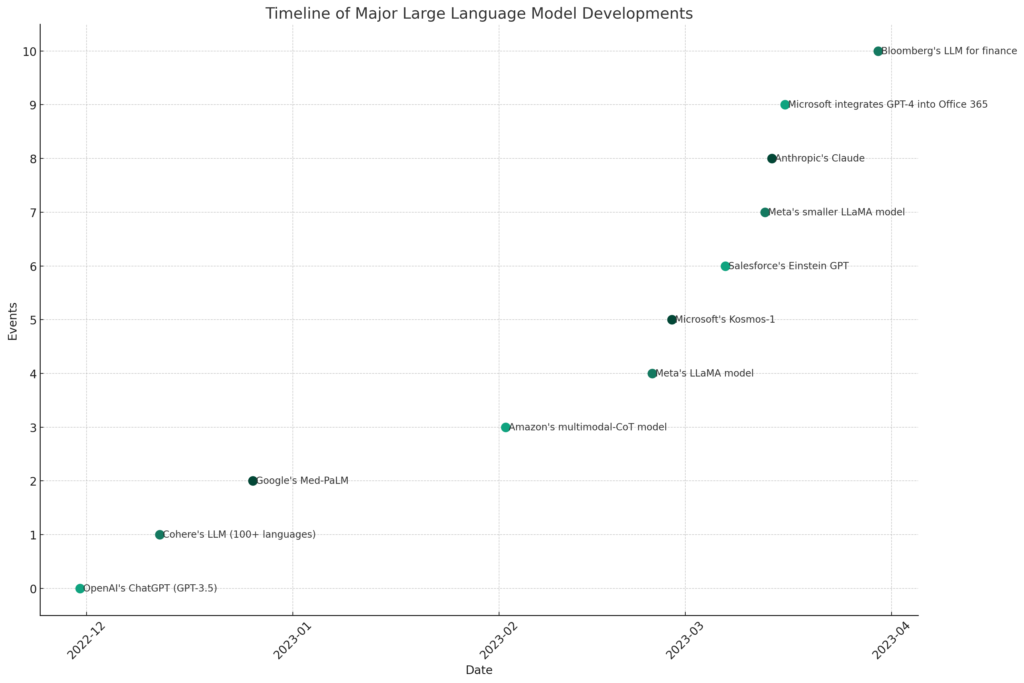
Here’s a timeline diagram illustrating the major developments in large language models (LLMs) following the launch of OpenAI’s ChatGPT. The diagram highlights key milestones from various organizations, including OpenAI, Amazon, Salesforce, Anthropic, Bloomberg, Microsoft, Cohere, and Google. Each event is marked with its date and a brief description, providing a visual overview of the rapid evolution in the field of generative AI.
